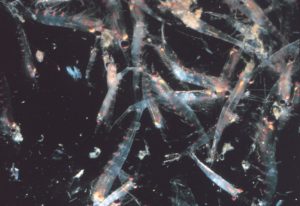
- Krill oil is oil from a tiny, shrimp-like animal. Baleen whales, mantas, and whale sharks eat primarily krill. In Norwegian, the word “krill” means “whale food.” People extract the oil from krill, place it in capsules, and use it for medicine.
Contents
Uses
- High cholesterol: Developing research shows that taking 1-1.5 grams of a specific krill oil product (Neptune Krill Oil, Neptune Technologies & Bioresources, Inc) daily reduces total cholesterol and “bad” low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and increases “good” high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol in patients with high cholesterol. Higher doses of 2-3 grams daily also appear to significantly reduce levels of triglyceride, another type of blood fat.
- Osteoarthritis: Early research shows that taking 300 mg of a specific krill oil product daily reduces pain and stiffness in people with osteoarthritis.
- Premenstrual syndrome (PMS): Early research shows that taking a specific krill oil product might reduce PMS symptoms.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Early research shows that taking 300 mg of a specific krill oil product daily reduces pain and stiffness in people with rheumatoid arthritis.
- Heart disease
- High levels of certain blood fats (triglycerides)
- High blood pressure
- Stroke
- Cancer
- Depression
- Painful menstrual periods.
Benefits
- Krill oil contains fatty acids similar to fish oil. These fats are thought to be beneficial fats that decrease swelling, lower cholesterol, and make blood platelets less sticky. When blood platelets are less sticky they are less likely to form clots.
Cautions
- Pregnancy and breast-feeding: Not enough is known about the use of krill oil during pregnancy and breast-feeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.
- Seafood allergy: Some people who are allergic to seafood might also be allergic to krill oil supplements. There is no reliable information showing how likely people with seafood allergy are to have an allergic reaction to krill oil; however, until more is known, avoid using krill oil or use it cautiously if you have a seafood allergy.
- ‘Surgery: Because krill oil can slow blood clotting, there is concern that it might increase the risk of bleeding during and after surgery. Stop using krill oil at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
Other names
Aceite de Krill, Acide Docosahexaénoïque, Acides Gras Oméga 3, Acides Gras N-3, Acides Gras Polyinsaturés, Acides Gras W3, Antarctic Krill Oil, Concentré de Protéines Marines, DHA, Docosahexanoic Acid, EPA, Euphausia Superba Oil, Euphausiacé, Euphausiids Oil, Huile d’ Euphausia Superba, Huile de Krill, Huile de Krill Antarctique, Huile d’Oméga 3, Marine Protein Concentrate, n-3 Fatty Acids, Omega 3, Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Omega-3, Oméga 3, Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Omega-3 Oil, Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, W-3 Fatty Acids.
References
Source: WebMD, “Krill Oil”, www.webmd.com/vitamins-supplements/