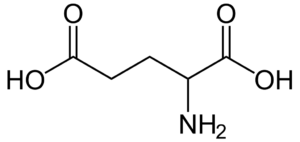
Glutamic acid (abbreviated as Glu or E; encoded by the codons GAA or GAG) is an ɑ-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins.
Contents
Uses
Glutamic acid is often used as a food additive and flavor enhancer in the form of its salt, known as monosodium glutamate.
Benefits
- Muscular Dystrophy: Glutamic acid may prove beneficial in the treatment of muscular dystrophy. A study performed at the DNA Laboratory at Guy’s Hospital in London showed that a deficiency of glutamic acid was found in the phenotype of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. The introduction of glutamic acid may reverse the defiency and promote a treatment for this disorder.
- Schizophrenia: Glutamic acid may also be an effective treatment for schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. A study performed at the Psychiatric Institute at the University of Illinois-Chicago revealed in a post mortem study that schizophrenics have a decreased level of glutamic acid. Introduction of glutamic acid therapy in order to reverse the deficiency may offer an effective therapy for this disorder.
- Parkinson’s Disease: Individuals who suffer from Parkinson’s disease are also deficient in glutamic acid. Research performed by the Department of Anatomy and Physiology at Boston University School of Medicine confirmed that individuals with Parkinson’s disease have a significantly lower glutamic acid levels than the control patients involved with the study. Glutamic acid therapy could be an effective treatment for Parkinson’s disease by regulating glutamic acid levels in the brain and reducing the effects of Parkinson’s disease.
- IQ for Mentally Challenged Individuals: Glutamic acid may also help mentally challenged individuals function at a higher level. According to the British Journal of Psychiatry, individuals with greatly reduced intelligence quotas were treated with glutamic acid for a period of 10 months. The results of the study showed that over the 10-month period, 50 percent of the individuals treated with glutamic acid improved their intelligence quota by eight to 11 points opposed to no change in the group not treated with glutamic acid.
Cautions
- An excess of glutamic acid from supplements may cause overstimulation of nerve receptors and contribute to neurological disorders such as epilepsy and Lou Gehrig’s disease.
- High doses of glutamic acid or glutamine may interfere with anti-epileptic medications. People with any type of neurological disorder, kidney or liver disease should consult their health-care provider before taking glutamic acid supplements.
Interactions
Unknown, please consult with your doctor.
Other names
2-Aminoglutaric acid, Glu or E
Reference
Source: LiveStrong, http://www.livestrong.com/article/480808-the-dangers-of-glutamic-acid-supplements/
LiveStrong, http://www.livestrong.com/article/320338-glutamic-acid-benefits/
Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glutamic_acid