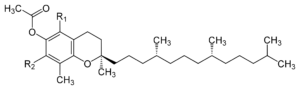
Vitamin E is a vitamin that dissolves in fat. It is found in foods such as cereals, vegetable oils, eggs, poultry, meat, vegetables, fruits, and wheat germ oil. Vitamin E is also available as a supplement.
Contents
Uses
- Some people use vitamin E for treating and preventing diseases of the heart and blood vessels including hardening of the arteries, chest pain, heart attack, leg pain due to blocked arteries, and high blood pressure.
- Vitamin E is also used for treating diabetes and its complications. It is used for preventing cancer, specifically lung and oral cancer in smokers; colorectal cancer and polyps; and gastric, prostate, and pancreatic cancer.
- Some people use vitamin E for diseases of the brain and nervous system including Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias, Parkinson’s disease, night cramps, restless leg syndrome, and for epilepsy, along with other medications. Vitamin E is also used for Huntington’s chorea, and other disorders involving nerves and muscles.
- Women generally use vitamin E for preventing complications in late pregnancy due to high blood pressure, PMS, painful periods, menopausal syndrome, hot flashes associated with breast cancer, and breast cysts.
- Sometimes vitamin E is used to lessen the harmful effects of medical treatments such as dialysis and radiation.
- Vitamin E is sometimes used for improving physical endurance, increasing energy, reducing muscle damage after exercise, and improving muscle strength.
- Vitamin E is also used for cataracts, aging skin, respiratory infections, skin disorders, asthma, sunburns, cystic fibrosis, infertility, impotence, chronic fatigue syndrome, peptic ulcers, for certain inherited diseases and to prevent allergies.
- Some people apply vitamin E to their skin to keep it from aging and to protect against the skin effects of chemicals used for cancer therapy (chemotherapy).
- The American Heart Association recommends obtaining antioxidants, including vitamin E, by eating a well-balanced diet high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains rather than from supplements until more is known about the risks and benefits of taking supplements.
- In cosmetics and personal care products, Tocopherol and other ingredients made from Tocopherol, including Tocopherol esters are used in the formulation of lipstick, eye shadow, blushers, face powders and foundations, moisturizers, skin care products, bath soaps and detergents, hair conditioners, and many other products.
- Tocopherol, Tocophersolan, Tocopheryl acetate, Tocopheryl Linoleate, Tocopheryl Linoleate/Oleate, Tocopheryl Nicotinate, Tocopheryl Succinate, Dioleyl Tocopheryl Methylsilanol and Potassium Ascorbyl Tocopheryl Phosphate all function as antioxidants. Tocopherol, Tocopheryl Acetate, Tocopheryl Linoleate, Tocopheryl Linoleate/Oleate, Tocopheryl Nicotinate and Dioleyl Tocopheryl Methylsilanol also function as skin-conditioning agents.
Benefits
- Vitamin E is an important vitamin required for the proper function of many organs in the body. It is also an antioxidant. This means it helps to slow down processes that damage cells.
- Counteract Vitamin E deficiency.
- Anemia in people having hemodialysis.
- Chest pain (angina)
- Hot flashes in people who have had breast cancer
- Hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis)
- Breathing problems in newborns
- Lung infections in elderly persons
- Heart failure
- Treating muscle diseases called Duchenne muscular dystrophy and myotonic dystrophy.
- High blood pressure.
- Helping people walk without pain when they have a disease called intermittent claudication.
- A type of arthritis called osteoarthritis. Vitamin E does not seem to decrease pain or stiffness and does not seem to prevent osteoarthritis from getting worse.
- Head and neck cancer
- Sores in the mouths of people who smoke
- Cancer of the pancreas
- Pharyngeal cancer
- Reducing scarring after surgery
- Colorectal cancer
- An eye condition called retinitis pigmentosa.
Cautions
- Vitamin E is generally safe for most healthy people when taken by mouth or applied to the skin. Most people do not experience any side effects when taking the recommended daily dose, which is 15 mg.
- Vitamin E is probably unsafe if taken in high doses. If you have a condition such as heart disease or diabetes, don’t take doses of 400 IU/day or more. Some research suggests that high doses might increase the chance of death and possibly cause other serious side effects. The higher the dose, the greater the risk of serious side effects.
- There is some concern that vitamin E might increase the chance of having a serious stroke called hemorrhagic stroke, which is bleeding into the brain. Some research shows that taking vitamin E in doses of 300-800 IU each day might increase the chance of this kind of stroke by 22%. However, in contrast, vitamin E might decrease the chance of having a less severe stroke called an ischemic stroke.
- There is contradictory information about the effect of vitamin E on the chance of developing prostate cancer. Some research suggests that taking large amounts of a multivitamin plus a separate vitamin E supplement might actually increase the chance of developing prostate cancer in some men.
- High doses can also cause nausea, diarrhea, stomach cramps, fatigue, weakness, headache, blurred vision, rash, and bruising and bleeding.
- Pregnancy and breast-feeding: When used in the recommended daily amount, vitamin E is probably safe for pregnant and breast-feeding women. There has been some concern that taking vitamin E supplements might be harmful to the fetus when taken in early pregnancy. But it is too soon to know if this is an important concern. Until more is known, do no take vitamin E supplements during early pregnancy without talking with your healthcare provider.
- Angioplasty: Avoid taking supplements containing vitamin E or other antioxidant vitamins immediately before and following angioplasty. These vitamins seem to interfere with proper healing.
- Low levels of vitamin K (vitamin K deficiency): Vitamin E might worsen clotting problems in people whose levels of vitamin K are too low.
- An eye condition called retinitis pigmentosa: All-rac-alpha-tocopherol (synthetic vitamin E) 400 IU seems to speed vision loss in people with retinitis pigmentosa. However, much lower amounts (3 IU) don’t seem to produce this effect. If you have this condition, it’s best to avoid vitamin E.
- Bleeding disorders: Vitamin E might make bleeding disorders worse. If you have a bleeding disorder, avoid taking vitamin E supplements.
- Head and neck cancer: Don’t take vitamin E supplements in doses of 400 IU/day or more. Vitamin E might increase the chance that cancer will return.
- Prostate cancer: There is concern that taking vitamin E might increase the chance of developing prostate cancer. The effect of vitamin E in men who currently have prostate cancer is not clear. But, in theory, taking vitamin E supplements might worsen prostate cancer in men who already have it.
- Surgery: Vitamin E might increase the risk of bleeding during and after surgery. Stop using vitamin E at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
Interactions
Moderate Interaction – Be cautious with this combination
- Cyclosporine (Neoral, Sandimmune) interacts with VITAMIN E
- Medications changed by the liver (Cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) substrates)
- Medications for cancer (Chemotherapy)
- Medications that slow blood clotting (Anticoagulant / Antiplatelet drugs)
- Medications used for lowering cholesterol (Statins)
- Niacin
- Warfarin (Coumadin)
Other Names
Acétate d’Alpha Tocophérol, Acétate d’Alpha Tocophéryl, Acétate de D-Alpha-Tocophéryl, Acétate de DL-Alpha-Tocophéryl, Acétate de Tocophérol, Acétate de Tocophéryl, Acétate de Vitamine E, All Rac-Alpha-Tocopherol, All-Rac-Alpha-Tocophérol, Alpha-Tocophérol, Alpha Tocopherol Acetate, Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate, Alpha tocotrienol, Alpha tocotriénol, Alpha-tocopherol, Alpha-Tocophérol, Beta tocotrienol, Bêta-tocotriénol, Beta-tocopherol, Bêta-tocophérol, Concentré de Tocotriénol, D-Alpha Tocopherol, D-Alpha Tocophérol, D-Alpha Tocopheryl Succinate, D-Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate, D-Alpha Tocotrienol, D-Alpha Tocotriénol, D-Alpha-Tocopherol, D-Alpha-Tocophérol, D-Alpha-Tocopheryl Acetate, D-Alpha-Tocopheryl Acid Succinate, D-Alpha-Tocopheryl Succinate, D-Alpha-Tocopheryl, D-Alpha-Tocophéryl, D-Beta-Tocopherol, D-Bêta-Tocophérol, D-Delta-Tocopherol, D-Delta-Tocophérol, Delta Tocotrienol, Delta-Tocotriénol, Delta-tocopherol, Delta-tocophérol, D-Gamma Tocotrienol, D-Gamma-Tocotriénol, D-Gamma-Tocopherol, D-Gamma-Tocophérol, DL-Alpha-Tocopherol, DL-Alpha-Tocophérol, DL-Alpha-Tocopheryl Acetate, DL-Alpha-Tocopheryl, DL-Alpha-Tocophéryl, DL-Tocopherol, DL-Tocophérol, D-Tocopherol, D-Tocophérol, D-Tocopheryl Acetate, Fat-Soluble Vitamin, Gamma tocotrienol, Gamma-tocotriénol, Gamma-tocopherol, Gamma-tocophérol, Mixed Tocopherols, Mixed Tocotrienols, Palm Tocotrienols, Rice Tocotrienols, RRR-Alpha-Tocopherol, RRR-Alpha-Tocophérol, Succinate Acide de D-Alpha-Tocophéryl, Succinate Acide de Tocophéryl, Succinate de D-Alpha-Tocophéryl, Succinate de Tocophéryl, Succinate de Vitamine E, Tocopherol Acetate, Tocopherol, Tocophérol, Tocophérols Mixtes, Tocotriénols de Palme, Tocotriénols de Riz, Tocotriénols Mixtes, Tocopheryl Acetate, Tocopheryl Acid Succinate, Tocopheryl Succinate, Tocotrienol, Tocotriénol, Tocotrienol Concentrate, Tocotrienols, Tocotriénols, Vitamin E Acetate, Vitamin E Succinate, Vitamina E, Vitamine E, Vitamine Liposoluble, Vitamine Soluble dans les Graisses.
References
Source: WebMd, “Vitamin E”, www.webmd.com/vitamins-supplements/
See Also” Tocopheryl acetate