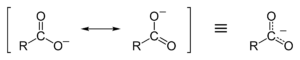
Carboxylate is a salt or ester of a carboxylic acid. A carboxylate ion is the conjugate base of a carboxylic acid, RCOO−. It is an ion with negative charge.
Contents
Uses
- The carboxylate ion is more stable. In contrast, an alkoxide ion, once formed, would have a strong negative charge on the oxygen atom, which would make it difficult for the proton to escape. Carboxylic acids thus have a lower pH than alcohols: the higher the number of protons in solution, the lower the pH.
Benefits
- The carboxylic acid group benefits from the combined effects of the carbonyl, with its polar nature, as well as those of the alcohols, with the O–H bond making it possible for (strong) hydrogen bonding to occur. This is so important in carboxylic acids that they often associate with H-bonding, behaving as though they were true dimers e.g. in non-polar solvents as well as in vapour phase
Cautions
-
n/a
Interactions
- Not known.
Other names
- n/a
References
Source: Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carboxylate