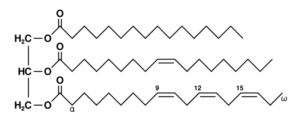
1,2,3-Propanetriol Trioctanoate known as Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) are triglycerides whose fatty acids have an aliphatic tail of 6–12 carbon atoms.
Contents
Uses
- MCTs are used along with usual medications for treating food absorption disorders including diarrhea, steatorrhea (fat indigestion), celiac disease, liver disease, and digestion problems due to partial surgical removal of the stomach (gastrectomy) or the intestine (short bowel syndrome).
- MCTs are also used for “milky urine” (chyluria) and a rare lung condition called chylothorax. Other uses include treatment of gallbladder disease, AIDS, cystic fibrosis, Alzheimer’s disease, and seizures in children.
- Athletes sometimes use MCTs for nutritional support during training, as well as for decreasing body fat and increasing lean muscle mass.
- MCTs are sometimes used as a source of fat in total parenteral nutrition (TPN). In TPN, all food is delivered intravenously (by IV). This type of feeding is necessary in people whose gastrointestinal (GI) tract is no longer working.
- Intravenous MCTs are also given to prevent muscle breakdown in critically ill patients.
Benefits
- MCTs passively diffuse from the GI tract to the portal system (longer fatty acids are absorbed into the lymphatic system) without requirement for modification like long-chain fatty acids or very-long-chain fatty acids. In addition, MCTs do not requirebile salts for digestion. Patients who have malnutrition, malabsorption or particular fatty-acid metabolism disorders are treated with MCTs because MCTs do not require energy for absorption, use, or storage.
- Medium-chain triglycerides are generally considered a good biologically inert source of energy that the human body finds reasonably easy to metabolize. They have potentially beneficial attributes in protein metabolism, but may be contraindicated in some situations due to a reported tendency to induce ketogenesis and metabolic acidosis. However, there is other authority reporting no risk of ketoacidosis or ketonemia with MCTs at levels associated with normal consumption.
- Due to their ability to be absorbed rapidly by the body, medium-chain triglycerides have found use in the treatment of a variety of malabsorption ailments. MCT supplementation with a low-fat diet has been described as the cornerstone of treatment forWaldmann disease. MCTs are an ingredient in some specialised parenteral nutritional emulsions in some countries (not USA). Studies have also shown promising results for epilepsy through the use of ketogenic dieting. Select studies have shown promising results for neurodegenerative disorders (e.g. Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases) but clinical effectiveness is not yet established.
Cautions
- MCTs are safe for most people when taken by mouth or given intravenously (by IV). They can cause diarrhea, vomiting, irritability, nausea, stomach discomfort, intestinal gas, essential fatty acid deficiency, and other side effects. Taking MCTs with food might reduce some side effects.
- Special Precautions & Warnings:
- Pregnancy and breast-feeding: Not enough is known about the use of MCTs during pregnancy and breast-feeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.
- Diabetes: MCTs can cause certain chemicals called ketones to build up in the body. This can be a problem for people with diabetes. Avoid using MCTs if you have diabetes.
- Liver problems: Because MCTs are processed primarily by the liver, they can cause serous problems in people with liver disease. Do not use MCTs if you have cirrhosis or other liver problems.
Interactions
None known.
Other names
1,2,3-Propanetriol Trioctanoate, AC-1202, Acide Caprique, Acide Caproïque, Acide Caprylique, Acide Laurique, Capric Acid, Caproic Acid, Caprylic Acid, Caprylic Triglycerides, Lauric Acid, MCT, MCT’s, MCTs, Medium-Chain Triacylglycerols, Medium-Chain Triglycerides, TCM, Triacylglycérols à Chaîne Moyenne, Tricaprylin, Triglycérides à Chaîne Moyenne, Triglycérides Capryliques, Triglicéridos de Cadena Media (TCMs), Trioctanoin
References
Source: Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Medium-chain_triglyceride
WebMD, http://www.webmd.com/vitamins-supplements/ingredientmono-915-medium+chain+triglycerides.aspx