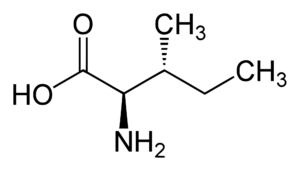
Isoleucine (abbreviated as Ile or I) encoded by the codons AUU, AUC, and AUA is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins.
Contents
Uses
- Isoleucine is found in especially high amounts in meats, fish, cheese, most seeds and nuts, eggs, chickens and lentils.
- In the human body Isoleucine is concentrated in the muscle tissues.
- It is necessary for hemoglobin formation and in stabilizing and regulating blood sugar and energy levels. A deficiency of isoleucine can produce symptoms similar to those of hypoglycemia.
Benefits
- It is one of several essential amino acids needed in the diet; human beings cannot synthesize it from simpler metabolites. Young adults need about 20 mg of this amino acid per day per kg (or about 8 mg per lb) of body weight. Isoleucine can be degraded into simpler compounds by the enzymes of the body.
- It is used in the body to produce certain biochemical compounds that help in energy production and has been found experimentally to reduce twitching and tremors in animals. The branched-chain amino acids (BCAA)?isoleucine, leucine, and valine?have been used as supplements for body (muscle) building.
- Both aerobic exercise and strength training increase protein requirements although they do so for different reasons. During aerobic exercise, AAs can be used for energy production (especially the branch-chain AA’s, leucine, isoleucine, and valine) and may provide up to 10% of the total energy produced during long-duration activity.
Cautions
Both a deficiency and an overdose can result in negative side effects.
Interactions
Unknown, please consult with your doctor.
Other names
2-Amino-3-methylpentanoic acid
References
Source: Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Isoleucine
LiveStrong, http://www.livestrong.com/article/435085-the-function-of-isoleucine-amino-acids/
Diet-and-health, http://www.diet-and-health.net/Supplements/Isoleucine.html